Study population
This study employed data from four consecutive survey cycles conducted between 1999 and 2006, including all NHANES database records with reported endometriosis. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a nationally representative cross-sectional study conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) with a focus on assessing the health and nutritional status of the United States population. It covers a broad spectrum of topics, ranging from demographic data, socioeconomic indicators, dietary patterns, to various health parameters, and employs rigorous methodologies for data collection, including medical and dental evaluations, physiological assessments, and laboratory analyses carried out by skilled healthcare professionals. The primary objective of the survey is to elucidate the prevalence and determinants of key health issues in the U.S. population and furnish evidence-based support for public health policy decisions. For more detailed information, kindly refer to the official website at https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm.
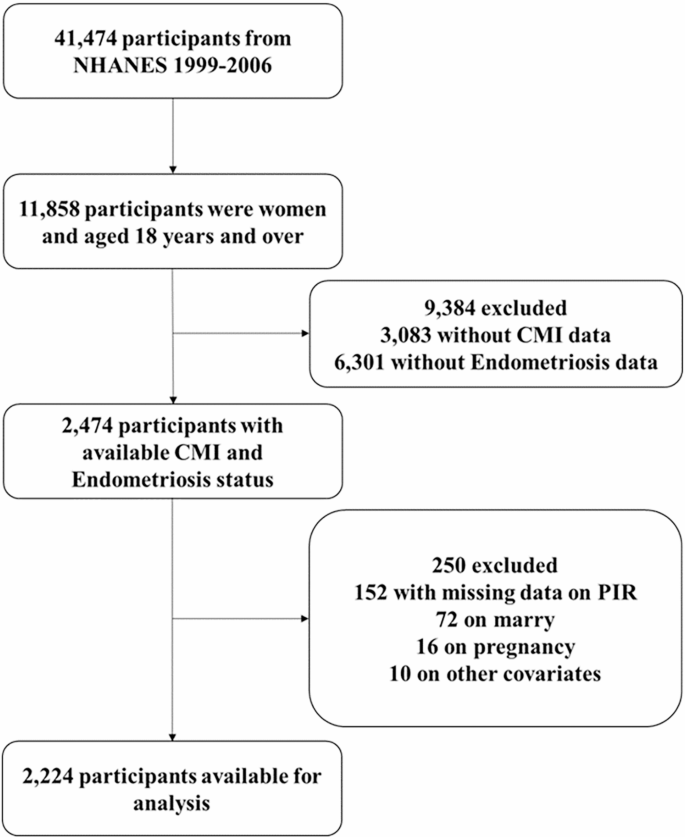
This study encompassed all participants from the 1999 to 2006 period, amounting to a total of 2,224 individuals. The participants included in this analysis possessed comprehensive demographic information, standard anthropometric measurements, lipid profiles, as well as details regarding reproductive and medical conditions. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) age < 18 years; (2) male; (3) lack of endometriosis diagnosis or data for calculating CMI; (4) missing covariate data, including marry, estrogen/progestin use, contraceptive use, pregnancy, alcohol consumption, smoking, BMI, Poverty Income Ratio (PIR), diabetes, coronary heart disease, angina, stroke, and heart attack status. The flowchart of this process is shown in Fig. 1.
Exposure variable: CMI
The CMI is computed utilizing the waist-to-height ratio and lipid profile of the participants. The formula is as follows: CMI = TG/HDL-C × WHtR. WHtR = waist circumference/height [16].
Outcome variable: Endometriosis
In the NHANES study, data regarding endometriosis was collected from participants’ health questionnaires, specifically relying on their answer to the inquiry, “Have you ever been diagnosed with Endometriosis by a healthcare provider?” An affirmative answer classified the individual as an endometriosis patient. While establishing the primary study outcome using questionnaire responses may introduce some level of uncertainty, the absence of direct diagnostic evidence like hysteroscopy or ultrasound in the NHANES dataset presents challenges in accurately identifying Endometriosis cases. Nonetheless, prior research has validated the feasibility and acceptance of utilizing questionnaires to ascertain the presence of Endometriosis in NHANES participants [17,18,19,20].
Covariates
To demonstrate the independent association between CMI and endometriosis, adjusted for potential covariates that might influence the association between CMI and endometriosis based on clinical relevance, including sociodemographic factors, reproductive status, medication use, and health conditions. The sociodemographic and lifestyle-related variables included in the analysis encompassed age (years), race (Mexican, American/Other Hispanic, Non-Hispanic White, Non-Hispanic Black, Other race), marital status (Married, Unmarried), education level (Less than 9th grade, 9–11th grade, High school, Some college, College graduate), pregnancy status, Poverty Income Ratio (PIR), smoking status (categorized as no for participants who smoked < 100 cigarettes in their lifetime and yes for participants who smoked > 100 cigarettes in their lifetime), and alcohol consumption (categorized as no for participants who consumed < 12 alcoholic beverages in the past 12 months and yes for participants who consumed at least 12 alcoholic beverages in the past 12 months). Medication utilization and reproductive status variables comprised contraceptive usage, estrogen/progestin therapy, and age at menarche, with information collected from the NHANES Questionnaire Data.
Body mass index (BMI, kg/m²), height, waist circumference, diabetes, stroke, coronary artery disease, angina, myocardial infarction, triglyceride (TG) levels, and directly measured high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) were all regarded as critical indicators of individual health status. Height, waist circumference, and BMI were objectively assessed by trained professionals at the Mobile Examination Center (MEC), with BMI computed as the individual’s weight (kg) divided by the square of their height (m²). Cholesterol levels were determined through serum samples sent to the University of Minnesota for specialized processing and analysis, following detailed protocols outlined in the NHANES Laboratory Procedures Manual. Information regarding diabetes, coronary heart disease, angina, stroke, and myocardial infarction was self-reported by participants via questionnaires.
Statistical analysis
To accommodate the intricate design elements of the NHANES survey, including oversampling techniques for specific populations, managing non-response, and stratified adjustments according to U.S. Census data, a sophisticated weighting mechanism is implemented to uphold the representativeness and precision of the data. In this study, pertinent sampling weights were applied throughout all statistical analyses. The fundamental characteristics of the survey participants were stratified into two groups based on the presence or absence of endometriosis. Continuous measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, whereas categorical variables were depicted as percentages to provide a comprehensive overview of each group’s characteristics. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and weighted chi-square tests were conducted to assess discrepancies in baseline continuous and categorical variables, respectively.
A multivariate logistic regression model was utilized to explore the association between CMI and endometriosis, with three models: Model 1 (unadjusted), Model 2 (adjusted for age and race), and Model 3 (adjusted for all covariates). After adjusting for covariates, a smoothed curve fitting analysis was conducted. A threshold effect analysis model was applied to investigate the relationship and identify inflection points between CMI and endometriosis. Finally, subgroup analysis was carried out to stratify the population based on different criteria, such as age, race, marriage, education level, PIR, BMI, smoking, alcohol consumption, pregnancy, contraceptive use, estrogen/progesterone use, coronary heart disease, angina, heart attack, stroke and diabetes. Interaction terms were incorporated to evaluate heterogeneity among subgroups. All statistical analyses were conducted using R (version 4.2.1) and EmpowerStats (version 2.0). A significance level of P < 0.05 was employed to determine statistical significance.



Add Comment